Because of their effectiveness, dependability, and adaptability to a wide range of applications, brushless DC (BLDC) motors have grown in popularity. The performance and operation of a BLDC motor significantly depend on the number of phases it employs. This article will comprehensively compare 3-phase, 2-phase, and single-phase BLDC motors, focusing on their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications. Additionally, we’ll include data charts to visualize their performance and usage better.
Overview of Brushless DC Motors
A direct current source drives synchronous brushless DC motors through an electronic controller. BLDC motors do not require brushes for commutation. Instead, they employ electrical commutation, which improves efficiency and reduces wear and tear.
Key characteristics of BLDC motors include:
- High power density
- Long lifespan
- Low maintenance requirements
- High efficiency
The number of phases in a BLDC motor affects how the magnetic fields are generated and how torque is delivered, leading to differences in performance characteristics.
Single-Phase BLDC Motors
Structure and Working Principle
Single-phase BLDC motors have a simpler design with a single winding in the stator. An alternating current waveform produced by the electronic controller interacts with the rotor’s permanent magnets to produce motion. These motors usually rely on additional mechanisms, like starting coils, to initiate rotation since a single phase cannot independently produce a rotating magnetic field.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Applications:
- Fans
- Small pumps
- Household appliances
Two-Phase BLDC Motors
Structure and Working Principle
Two-phase BLDC motors use two sets of stator windings offset by 90 degrees. To produce a revolving magnetic field, the controller switches the current between these two windings. These motors offer a compromise between single-phase simplicity and three-phase performance.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Applications:
- Robotics
- Small precision devices
- Low-power industrial equipment
Three-Phase BLDC Motors
Structure and Working Principle
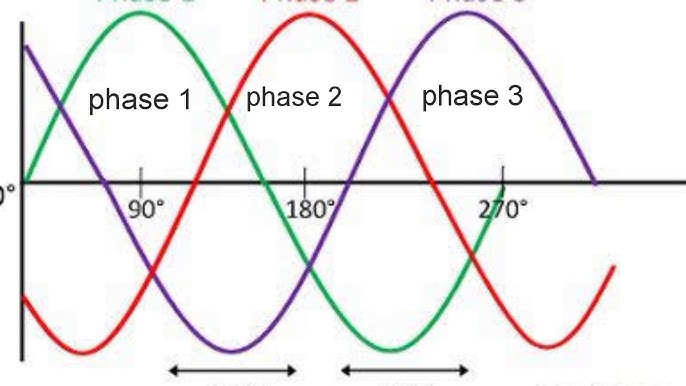
Three-phase BLDC motors feature three stator windings spaced 120 degrees apart. The electronic controller provides a three-phase alternating current to create a smooth and continuous rotating magnetic field. This design allows for high performance and precision.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Applications:
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Aerospace systems
- Industrial automation
- Medical equipment
Gian Featured Product
Comparison of 3 Phase, 2 Phase, and Single Phase BLDC Motors
The main distinctions between the three kinds of BLDC motors are outlined in the table below:
| Feature | Single-Phase | Two-Phase | Three-Phase |
| Efficiency | Low | Moderate | High |
| Torque Ripple | High | Moderate | Low |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Complexity | Simple | Moderate | Complex |
| Applications | Household appliances | Robotics, small devices | EVs, industrial systems |
| Starting Mechanism | Requires starting coil | Direct start | Direct start |
| Power Density | Low | Moderate | High |
| Noise & Vibration | High | Moderate | Low |
Efficiency Comparison
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are highly efficient and versatile. The efficiency of 3-phase, 2-phase, and single-phase BLDC motors depends on the application and operational conditions.
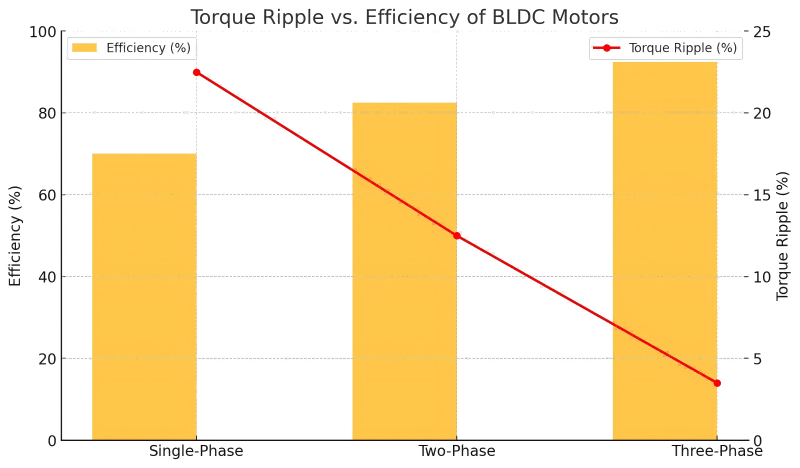
- 3-Phase BLDC Motors: These are the most efficient due to balanced power delivery, smooth operation, and low torque ripple. Their robust design offers excellent performance in high-power and high-speed applications, such as industrial automation and electric vehicles.
- 2-Phase BLDC Motors: 2-phase motors are less efficient than 3-phase motors because they produce higher torque ripple and require more complex drive electronics to achieve smooth performance. However, they are cost-effective and suitable for applications requiring moderate precision and efficiency, such as small appliances.
- Single-Phase BLDC Motors: These are the least efficient among the three due to significant torque ripple and uneven power distribution. They are simpler in construction and are ideal for low-power, low-cost applications like fans and pumps, where high efficiency is less critical.
Torque Ripple Comparison
Torque ripple is a critical performance factor in Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, influencing efficiency, noise, and vibration. It arises due to variations in torque production during rotor rotation, primarily caused by non-sinusoidal back-EMF, commutation events, and magnetic design.
- Three-Phase BLDC Motors: These motors exhibit the lowest torque ripple among the three configurations. Their design ensures smoother operation as the torque-producing phases overlap, minimizing pulsations. Additionally, they provide superior efficiency and reduced acoustic noise, making them ideal for precision applications like robotics and medical devices.
- Two-Phase BLDC Motors: Torque ripple is higher in two-phase motors than in three-phase due to the lack of overlapping torque generation phases. This results in uneven power delivery, leading to more vibrations and noise. However, these motors are simpler and cheaper, often used in cost-sensitive applications.
- Single-Phase BLDC Motors: Single-phase motors have the highest torque ripple because only one phase contributes to torque at a time. The intermittent nature of torque generation causes pronounced pulsations, leading to significant vibration and noise. They are yet small and appropriate for low-power applications where size and cost are crucial considerations.
Chart: Torque Ripple vs. Efficiency
Choosing the Right Motor
Selecting the right type of BLDC motor for your application depends on your priorities in terms of performance, efficiency, cost, and control.
- Performance-Oriented Applications: If you need a motor for an application that requires high performance, smooth torque, and high efficiency—such as in electric vehicles or industrial robotics—a 3-phase BLDC motor is the ideal choice.
- Moderate Performance at a Lower Cost: For applications where performance requirements are moderate, but cost and simplicity are more important, a 2-phase BLDC motor may be a good option. It is suitable for fans or small tools where the torque ripple is acceptable.
- Cost-Effective Simple Solutions: For small appliances where cost is the primary factor, and the performance limitations are acceptable, single-phase BLDC motors are the best choice. These motors are easy to control, inexpensive, and suitable for non-critical applications.
When comparing 3-phase, 2-phase, and single-phase brushless DC motors, the choice depends on application needs. 3-phase brushless DC motors are ideal for high-performance applications due to smoother operation and better efficiency. 2-phase motors offer a simpler design but may result in more vibration, suitable for cost-sensitive applications. Single-phase motors, though compact and affordable, provide less efficiency and torque, making them best for low-power tasks. For buyers seeking bulk options, wholesale brushless DC motors provide cost-effective solutions tailored to diverse performance requirements, ensuring the right motor type for various industrial or commercial uses.