In mechanical engineering, combining gearboxes and motors is essential for optimal industrial efficiency. The way gearboxes and motors are paired significantly impacts the overall system efficiency, performance, and longevity. In this article, we will explore the different methods of combining gearboxes and motors, focusing on optimizing efficiency in various systems, from industrial machinery to electric vehicles.
Understanding Gearboxes and Motors
Before diving into the different combinations, it’s essential to understand the roles of gearboxes and motors in a system.
Motor: Motors are widely used in industries, from automotive to robotics, providing the necessary power to perform mechanical tasks.
Gearbox: A gearbox modifies motor speed and torque to meet specific operational needs. Gearboxes are essential for controlling the output of a motor to ensure the desired performance characteristics, such as speed, torque, and efficiency, are achieved.
In systems where torque needs to be converted into high-speed motion or vice versa, a combination of the right gearbox and motor becomes indispensable for efficient operation.
Comparison of Different Gearbox Types
| Gearbox Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Planetary Gear | Compact, high torque, low backlash | Expensive, complex design |
| Worm Gear | High reduction ratio, self-locking | Low efficiency, limited to low speeds |
| Bevel Gear | Directional change, high-speed suitability | Requires precise alignment, complex design |
| Geared Motor | Compact, easy integration | Limited flexibility |
Types of Gearbox-Motor Combinations
There are several methods to combine gearboxes and motors depending on the application, the required output, and the operating conditions. Let’s explore the common methods.

Direct Drive Systems (Motor to Load)
In direct drive, the motor connects directly to the load. This method is often used in applications where high efficiency is required, and the motor’s speed is suitable for the application. This system avoids the mechanical losses typically introduced by gearboxes, making it a preferred choice in certain applications.
| Pros | Cons |
| Higher efficiency due to the lack of mechanical losses from a gearbox. | Limited torque control and adjustment. |
| Simple design with fewer components. | Higher motor size might be required for higher torque applications. |
| Suitable for applications where the motor speed matches the load speed. |

Geared Motor Systems (Motor with Integrated Gearbox)
A geared motor system is a combination of a motor and gearbox integrated into one unit. The motor’s output shaft is connected directly to the gearbox, which converts the motor’s speed to the required output speed and torque. Perfect for applications requiring compact design and ease of use.
| Pros | Cons |
| Compact design, ideal for space-constrained environments. | Limited flexibility in altering the motor and gearbox specifications. |
| Efficient torque conversion with precise control over speed. | Potentially higher cost due to the integrated design. |
| Offered in multiple configurations to suit specific application requirements. |
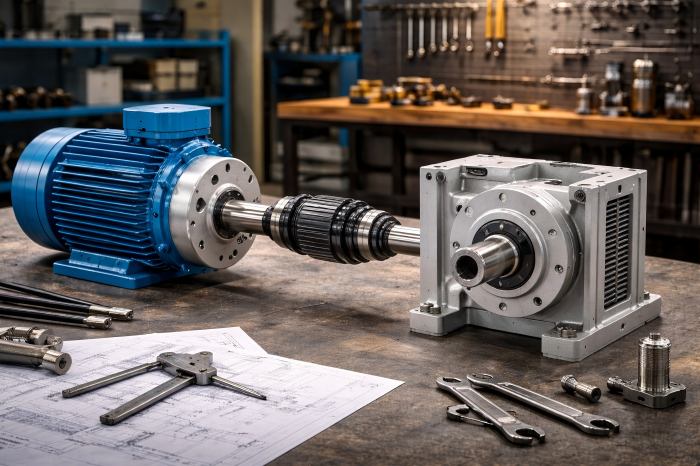

Separate Motor and Gearbox Systems (Flexible Pairing)
In this method, the motor and gearbox are separate components that are connected through shafts and couplings. This method offers the greatest flexibility in terms of selecting the most suitable motor and gearbox for the application. Motors with various specifications can be paired with gearboxes of different types, offering optimal combinations for a wide range of applications.
| Pros | Cons |
| Greater flexibility to choose the best motor and gearbox | Requires more space and additional components (e.g., couplings) |
| Easier to replace or upgrade individual components | More complex installation and maintenance processes |
| Customizable for various power and torque specifications |

Planetary Gear Systems with Motors
Planetary gear systems are a type of gearbox where multiple gears orbit a central gear, providing high torque output in a compact size. When combined with motors, planetary gear systems are ideal for high-performance applications that require compactness and high torque. They are popular in robotics, automotive, and aerospace for compactness and high torque.
| Pros | Cons |
| Compact and lightweight, suitable for high-torque applications. | Complex design can increase the cost. |
| Even torque distribution among multiple gears, reducing wear. | Requires precise manufacturing to ensure smooth operation. |
| High efficiency and low backlash. |
Gear Systems with Motors
Worm gear systems use a screw-like worm and a gear mesh to provide high reduction in compact sizes. These systems are commonly used when there is a need for significant speed reduction and high torque, such as in conveyors or lifting equipment.
| Pros | Cons |
| Excellent torque multiplication with high reduction ratios | Friction in worm gears results in lower efficiency |
| Self-locking nature, beneficial for preventing backdrive | |
| Simple design with minimal backlash |
Restricted to low-speed use due to the high reduction ratio

Bevel Gear Systems with Motors
Bevel gears are used in systems where the motor and load are at an angle to each other. Bevel gearboxes can be either straight or spiral, and they are often used in systems where direction change is needed, such as in automotive driveshafts or mechanical presses.
| Pros | Cons |
| Ideal for changing the direction of motion | More complex than parallel gear systems |
| Suitable for high-speed applications | Requires careful alignment to ensure efficiency |
| Less wear due to the angular arrangement of gears |
Factors to Consider When Combining Gearboxes and Motors
When selecting the optimal combination of gearboxes and motors, several factors should be considered to achieve optimal efficiency. These include:
Torque and Speed Requirements: The gearbox must match the motor’s torque output and desired speed. A high-speed motor with a low-torque gearbox will be ineffective for applications requiring high torque, and vice versa.
Efficiency Needs: Gearboxes introduce mechanical losses, so the combination of motor and gearbox should aim for maximum efficiency. For applications that require high efficiency, direct-drive systems or high-efficiency gearboxes should be considered.
Space Constraints: Space is often limited, especially in compact machinery or robotic systems. In such cases, integrated geared motors or planetary gear systems are ideal choices.
Cost Considerations: The complexity of the motor-gearbox combination affects cost. While integrated systems may be more expensive initially, separate systems may offer more flexibility for upgrades and replacements.
Operational Conditions: The environment in which the system operates can affect the choice of motor and gearbox.
Factors Affecting Gearbox-Motor Efficiency
| Factor | Impact on Efficiency |
| Torque and Speed Match | Maximizes power and efficiency |
| Gearbox Efficiency | Affects overall energy loss in the system |
| Motor Efficiency | Reduces energy consumption |
| System Size Constraints | Limits the design flexibility |
| Operational Conditions | Affects component longevity and reliability |
Optimizing Gearbox-Motor Combinations
To optimize efficiency, it’s essential to:
Match the Gearbox to the Motor’s Power Output: Over-sized or under-sized gearboxes can result in energy losses. Aligning motor power with the gearbox maximizes system efficiency.
Select Low-Backlash Gearboxes: Backlash can reduce the precision of mechanical systems, especially in robotics. Choosing gearboxes with minimal backlash ensures smoother motion and reduces energy losses.
Use High-Efficiency Motors: Pairing energy-efficient motors with well-designed gearboxes reduces overall energy consumption and operational costs.
Consider Variable Speed Drives (VSD): For applications where motor speed needs to vary, coupling a motor with a VSD and a suitable gearbox can provide energy savings and efficiency.
Selecting the right gearbox-motor combination is crucial for efficiency, considering torque, speed, space, and energy. Whether opting for direct drive, geared motors, planetary systems, or worm gears, the right pairing will significantly affect system performance and energy consumption. As industrial needs grow, optimized gearbox-motor pairings will be essential for high-performance, energy-efficient systems.